Ranking on search engines today isn’t just about fixing meta tags or building backlinks.
AI-generated content, changing user needs and preferences, and the fight for featured snippets have completely changed the game.
As an SEO professional or business owner, you’re probably feeling the pressure. Search engines roll out core updates regularly, and your competitors seem to be mastering advanced SEO tools, and old tricks no longer cut it.
So, where do you start?
Modern SEO demands a focused approach.
It centers on creating content that meets E-E-A-T standards and delivers real value to your audience.
Rather than chasing every tactic, focus on what search engines truly value: authentic expertise and user benefit.
Our agency has proven this approach works. We’ve guided hundreds of businesses to success with strategies built on these principles.
In this guide, you’ll learn what’s working in 2025 and beyond, why outdated methods fall short, and how to build an SEO strategy that’s built to last.
Search intent: Getting inside your audience’s mind
SEO solves user problems by understanding search intent. It’s the reason behind what people are looking for when they type something into a search engine.
To succeed today, you need to do more than provide basic answers. Your content should be purposeful, trustworthy, and thorough enough to help the searcher.
Understanding how search intent works
To rank and build visibility, align your content with search intent. Consider these examples:
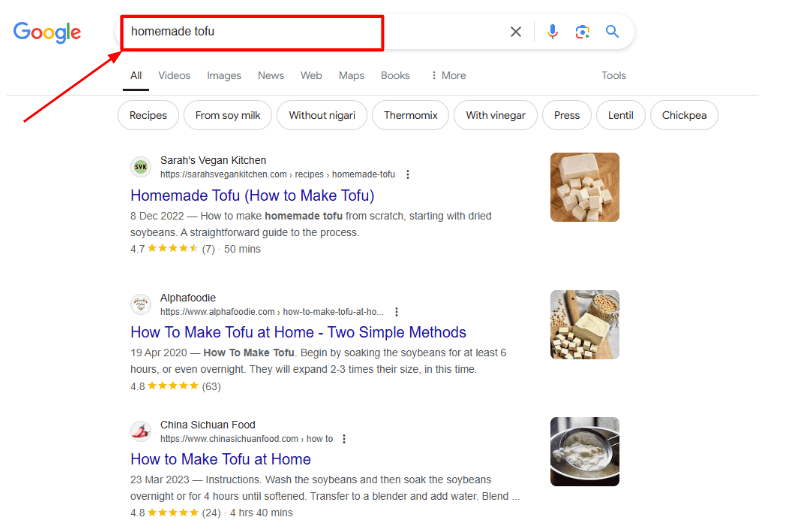
A search for “homemade tofu” returns recipes and videos because users want to make tofu at home, not buy it. However, searching “buy tofu” delivers eCommerce pages and product ads instead.
Screenshot provided by the author
Google understands you’re likely looking for recipes to make tofu at home. That’s why the top results are blog posts and videos. Not eCommerce pages selling tofu.
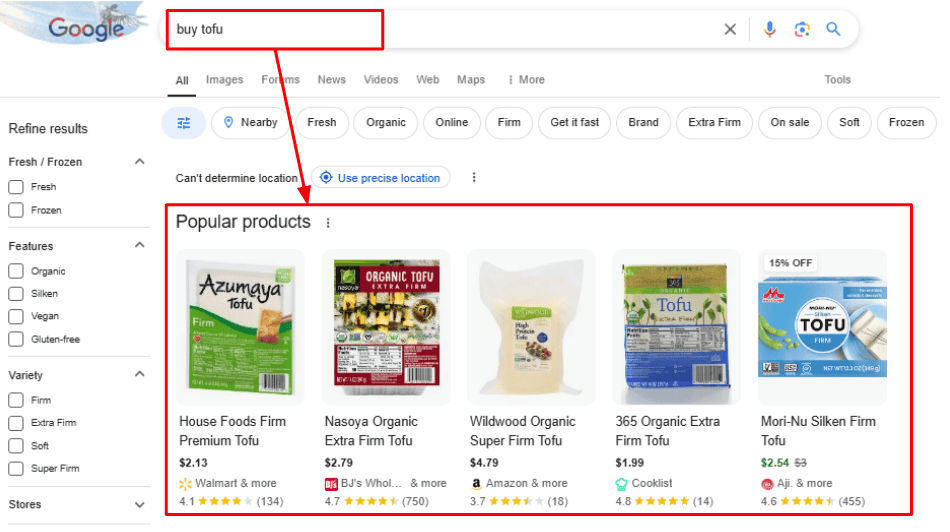
On the other hand, if you search “buy tofu,” the top results are eCommerce pages and product ads:
Screenshot provided by the author
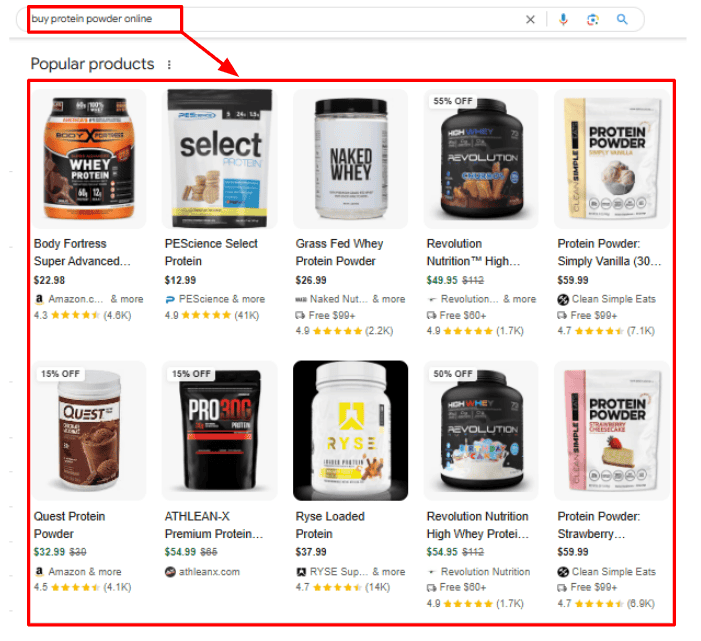
For instance, searching ‘buy protein powder online’ returns eCommerce product pages:
Screenshot provided by the author
On the other hand, ‘best protein powder for muscle gain’ often brings up blogs and product reviews:
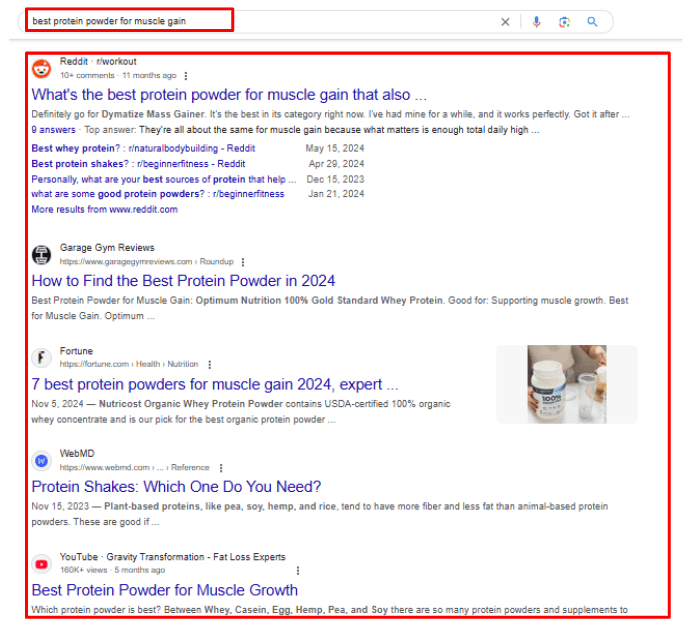
Screenshot provided by the author
Types of search intent (and how to address them)
We can classify search intent into four categories:
- Informational – When a searcher is interested in learning more about a topic (e.g., “What is plant-based food made of”). It would lead to a blog post, article, or FAQ page.
- Navigational – When a searcher wants to find a specific website or page (e.g., “WordPress admin login”). It should point directly to the login page without intermediate pages.
- Commercial – When the user is researching more about a product or service before making a purchasing decision (e.g., “best waist trainer”). It might display comparison blogs or product roundups.
- Transactional – When the user is ready to complete a transaction or purchase (e.g., “rent an RV”). It should lead directly to eCommerce product pages or checkout options.
How E-E-A-T supports search intent
Google prioritizes content that demonstrates E-E-A-T—Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
Quality content demands more than search rankings. It requires precision, authority, and relevance.
Expert contributors bring deep subject matter knowledge, while strong credentials validate your expertise. Build credibility with trust signals like client testimonials and secure infrastructure.
These principles make sure your content is accurate, reliable, and relevant. This helps your content rank higher and connect better with users.
Let’s break down the E-E-A-T components to focus on:
- Experience – Demonstrate that your content is written by subject matter experts (SMEs) with direct and first-hand experience on the topic. This allows you to provide unique insights based on your experiences.
- Expertise – Expertise refers to the creator’s skills, knowledge, and credentials. For example, readers will be more receptive to tax advice from a licensed CPA than a hobby blogger.
- Authoritativeness -Authority is the reputation you have in your industry. Google checks your site’s authority by analyzing your backlink profile. The more coverage, mentions, and quality backlinks you have, the more reputable your brand is.
- Trustworthiness – Google considers your site trustworthy if it’s honest, reliable, accurate, and safe. Ensure that your website is secure and that your content is accurate, truthful, and up-to-date. Also, include trust signals like customer testimonials, social proof, trust badges, and awards.
E-E-A-T isn’t exactly a ranking factor in the traditional sense. Think of it as a set of guidelines to help you create helpful and user-centered content.
The role of content depth in satisfying search intent
Content depth measures the level of detail, thoroughness, and richness of content. With the advent of AI-generated content, content depth is no longer about length.
It’s about the comprehensiveness with which your web pages cover certain topics. You can achieve a high level of comprehensiveness by:
- Including FAQs to answer users’ follow-up questions.
- Adding multimedia (e.g., infographics, videos) to illustrate complex ideas.
- Providing unique insights or original research to offer more than standard answers.
- Help search engines understand your content by using schema markup.
You need to understand what users are searching for. Then create content that answers their questions. But here’s the catch: even amazing content needs a solid foundation. If your website has technical problems, your content won’t reach its audience.
Technical SEO lays the groundwork for everything else. Search engines can effectively find, crawl, and index your content while still giving users a great experience.
Technical SEO made simple: What you need to know
Technical SEO can be tougher to master. Yet, it’s the foundation upon which you build your on-page and off-page SEO. Without the foundation, your whole project crumbles.
Start by fixing indexing and crawling issues before moving on to more detailed optimizations like Core Web Vitals.
This phased approach allows you to build a solid technical foundation without getting bogged down by too many changes at once.
Equip Yourself with the Right Tools
To get started, have tools like Google Search Console, Google Analytics & Bing Webmaster Tools, SEMrush, and Ahrefs.
Each of the tools mentioned plays a unique role in technical SEO. For instance, Google Search Console highlights crawling and indexing issues.
Google Analytics tracks your website traffic. SEMrush and Ahrefs analyze your competitors. Bing Webmaster Tools handles Microsoft search optimization.
Need more advanced tools? Screaming Frog and Sitebulb crawl your site deeply. GTmetrix checks your site speed. These tools work best for complex websites that need detailed analysis.
Together, they provide a comprehensive view to support and enhance your technical SEO efforts.
Avoid Common Technical SEO Mistakes
Pay attention to common SEO mistakes such as:
- Not setting up 301 redirects
- Failing to update sitemaps
- Neglecting broken links
Avoiding these is crucial for a smooth user and search engine experience.
After that, you need to understand the Core Web Vitals. These are three metrics that help you measure your web page’s interactivity, loading performance, and visual stability.
The three Core Web Vitals are:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – Measures how long the largest content element on your webpage takes to load. To provide a good user experience, you need to have an LCP of less than 2.5 seconds.
- Interaction To Next Paint (INP) – Previously known as First Input Delay (FID), INP measures your webpage’s responsiveness. You need to have an INP of less than 200 milliseconds to provide a good user experience.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Measures visual stability. You should have a CLS score of less than 0.1 to provide a good user experience.
Beyond their role as ranking factors, Core Web Vitals are fundamental to user experience (UX). These metrics directly influence user satisfaction and retention, impacting everything from bounce rates to conversion rates.
Good Core Web Vitals deliver a great user experience that keeps users engaged, which in turn contributes to better SEO outcomes.
Ensure mobile optimization
Given Google’s mobile-first indexing, it’s essential to ensure your technical SEO optimizations work on mobile devices as well.
Mobile-friendly schema markup, image compression, and responsive layout design are all crucial for achieving a smooth user experience across devices, which can boost your SEO performance.
Together, these Core Web Vitals make up a vital pillar of technical SEO since Google uses them as ranking factors. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, Search Console, and Lighthouse can help you optimize them.
Implement structured data
Structured data, also called schema markup, is code that helps search engines understand web pages. It tells them what each element is, its relevance, and how to understand it.
In short, structured data tells the bots, “This is a product,” “This is a video,” or “This is a GIF”.
By adding the right schema markup, your web pages can earn the featured snippet spot.
Different schema markups serve various content types. For example, a product schema is ideal for e-commerce, displaying essential information such as prices and availability.
Recipe schema highlights cooking times and ingredients, enhancing visibility for food blogs. By implementing relevant schema types, you increase the chances of appearing in SERP features like featured snippets and review stars, drawing users’ attention.
Such snippets are more appealing on the SERP with additional details under the title and description. They look like this:

Screenshot provided by the author
Those review stars wouldn’t appear on search results without schema markup.
Structured data helps bots index and potentially rank your pages. Besides, your pages stand out from others, which can improve your click-through rate (CTR).
With your technical SEO foundation in place, your site is now primed for the next step: on-page optimization. This is where you shift your focus to what users see and interact with—your content, keywords, and overall user experience.
3. Optimizing what users see: On-page SEO
Keyword optimization is the first thing that comes to most site owners’ minds when they think of on-page SEO. But on-page SEO goes beyond keyword research and placement.
One of the on-page optimization techniques you should focus on in 2025 is content structure.
As you develop and fine-tune your content (for both static pages and blog posts), you need to pay attention to:
Title tags
Also known as a meta title or SEO title, your title tag gives search engine algorithms an overview of what your page is about.
Screenshot provided by the author
Your title tag and H1 don’t always have to be similar. Generally, you need to keep it brief (50-60 characters), be unique, and make sure your target keyword is as close to the beginning of the title as possible.
Consider keeping your title tag keyword-focused for SEO while making the H1 more engaging and conversational.
This balance appeals to search engine algorithms while engaging users who land on the page, helping to increase dwell time.
Meta descriptions
Meta descriptions might not directly affect rankings on SERPs, but Google generates snippets based on them. Like title tags, they influence users’ decisions to click on your page, boosting your CTR.
Screenshot provided by the author
Aim for a meta description between 155-160 characters. Include your target and related keywords, and add a benefit to make it actionable.
Use action verbs like ‘Learn,’ ‘Discover,’ or ‘Explore’ to prompt action and increase engagement.
While AI can write meta descriptions, creating them yourself often works better. You can better match what users want and show the value of your page, leading to more clicks.
Header optimization
HTML header tags tell a browser what styling it should use to display your webpage. It breaks up your content into a hierarchical and logical structure.
Put relevant keywords in your headers to show search engines what your content covers. Headers also help readers scan your page and quickly find what they need.
Your header tags could look like this:
<h2>Your header here<h2>
They can go from <h1> to <h6>. <h1> tag is typically the most important text, which is your page’s title or main heading. <h2> and <h3> tags are mostly used for subheadings. <h4>, <h5>, and <h6> tags give these subsections more structure.
Internal linking strategy
Ideally, internal links keep visitors on your site by helping them find more information they might need. But there are great SEO benefits too.
Establish a ‘hub and spoke’ structure, where main pages (hubs) link to related supporting pages (spokes). This approach builds topical authority and makes it easier for users to find relevant information.
For example, a ‘Content Marketing Hub’ might link to SEO, email marketing, and analytics pages. This creates a clear path for users and helps your site rank better.
These internal links help search engines:
- Find all your pages
- Understand each page’s topic
- See how pages connect
- Know which pages matter most

When internally linking your web pages, be sure to use relevant, keyword-rich anchor texts.
Don’t forget to link back to your high-priority pages, such as product and service pages.
User experience elements
Google also considers user experience (UX) as part of its “people-first content” approach. There are three vital UX principles for SEO:
- Navigation optimization – Simple and intuitive site navigation is key. Complex structures may have worked for traditional SEO, but modern strategies focus on usability. A hub-and-spoke structure lets users explore your site easily. It organizes content logically, improving SEO.
- SEO-friendly layouts – Website aesthetics and SEO priorities can feel at odds. But you can balance user experience (UX) with organic traffic generation. Key elements like whitespace, color schemes, and layout play a big role. A well-designed page looks appealing and keeps users engaged. This boosts metrics like time on the page, brand searches, and click-through rates (CTR). Better engagement also supports your SEO goals..
- Mobile-friendly design – Most users rely on their phones to search for content and products they need. Google looks at your mobile site first to see whether it is responsive. Make your site work well on all devices to improve user experience and rankings.
On-page SEO focuses on optimizing content structure to improve the user experience. But building a strong online presence doesn’t stop there.
To improve you organic search visibility, you need to look beyond your own site. That’s where off-page SEO comes into play—building authority, trust, and visibility through external factors.
4. Beyond the page: off-page seo essentials
The work you do directly on your web pages is only half the effort. You need other techniques outside your site to maximize your off-site presence.
Search engines look at backlinks from trusted websites to judge your content’s quality. Sites that earn more quality backlinks tend to rank higher and get more traffic than their competitors.
Generally, there are a few modern link-building strategies to get quality backlinks to your site. One of them is digital PR.
Digital PR builds brand awareness and helps earn quality backlinks from trusted websites. This boosts your site’s authority and search rankings.
- Reaching out to the media,
- Getting sponsorships,
- Writing press releases,
- Working with influencers.
You can also earn backlinks by creating valuable resources like:
- In-depth guides
- Original research
- Interactive tools
These resources attract natural links without you having to ask for them.
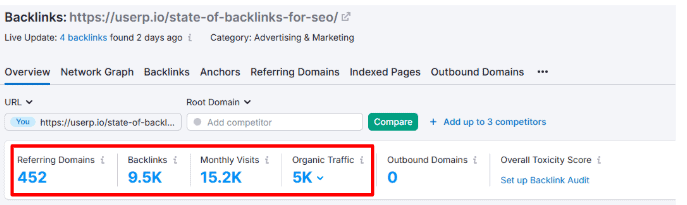
For example, this blog post on The State of Backlinks for SEO in 2025 is one of the top-performing resources on our website.
Semrush’s Backlink Analytics tool shows that this specific page has 9.5k links from 452 referring domains and receives an impressive 15.2k monthly visits.
Why do resources perform so well?
They contain a lot of information on a single page. The guide above constitutes a whopping 4,422 words. Long-form articles perform better on Google.
Secondly, such guides meet Google’s E-E-A-T principles. Our example above particularly included unique insights from 800+ SEO experts. People naturally link to it when they write about that specific topic.
Brand signals tell search engines and users they can trust you. Your online reputation comes from social proof, author credibility, and what others say about your business.
Your digital footprint builds trust through:
- Active social media accounts
- Verified business locations
- Mentions from trusted websites
Building brand signals and earning authority through off-page SEO are important steps, but how do you know if your efforts are paying off?
5. Track, measure, improve: The role of analytics
SEO takes considerable time, effort, and money. You want to measure ROI to see whether your tactics yield fruit.
You must look at your SEO analytics and track metrics to evaluate the success of the overall strategy and spot areas that need improvement.
Common tools you can use for SEO analytics include Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and Google Search Console.
Important SEO metrics to analyze include:
- Organic search traffic: This tells you if your strategy is bringing quality traffic from search results. Use GA4 to track organic traffic by heading to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic Acquisition.
- Average time on page – Engagement time shows how long people stay on your web pages. Measure this metric on GA4 by going to Reports > Engagement > Pages and Screens. You’ll find it under Average Engagement Time.
- Bounce rate: This metric displays the number of users who visit your web pages but leave without interacting with the site. It helps you assess the level of engagement and relevance of your content. It also helps you find and fix website issues like slow loading, irrelevant content, or poor mobile responsiveness.
Follow this path on Google Analytics to track your bounce rate: Reports > Life Cycle > Engagement > Pages and Screens. - Conversions: These happen when a user downloads an ebook, subscribes to your email list, signs up for a free trial, or completes a transaction. Google Analytics terms conversions as “key events.” You can view your key events on GA4 by going to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic Acquisition.
You can also track your site’s performance using Google’s Core Web Vitals, which we looked at in the Technical SEO section.
You can find these metrics on your Google Search Console account under the “Experience” section.
Conclusion
SEO is about more than just achieving high rankings in search engine result pages (SERPs).
Understanding and meeting user needs is key, along with keeping up with evolving search engine algorithms.
Search engines reward valuable and relevant content. Focus on meaningful, user-centered content with a strong technical foundation.
This guide outlines the key elements for success, such as:
- Understanding search intent,
- Embracing E-E-A-T,
- Ensuring your site is technically sound
However, SEO doesn’t stop there. Continuously improve content, enhance user experience, and build authority with off-page strategies.
By concentrating on these critical areas, you can lay a strong foundation for success. Building your site’s authority through link building can take a lot of time and effort. Let us take care of that for you so you can focus on what matters most. Book a call today, and let’s make your SEO strategy more effective and manageable.